IQVIA Vigilance Platform is our secure SaaS environment built to simplify safety and PV processes, while boosting speed, accuracy, and efficiency.






















- Blogs
- Steps to Success: Safety Surveillance Automation Assessment
The pharmaceutical industry continues to experience an explosion of data, due to the growth of new therapies, drugs and devices, and new data sources. In addition, data collection from wearable devices, social media, audio recordings and shared images are now being used to monitor the safety of products and treatments. As the use of these resources is expected to grow further, your safety organization must rethink its approach to automation to keep pace with this expansion and to streamline safety surveillance to more rapidly address issues.
Providing pharmaceutical companies with a thorough assessment of their current automation journey allows them to work towards achievable and scalable automation. IQVIA’s Safety Automation Maturity Matrix (SAMM) offers clear guidance on vetting preparedness for automation, identifying the most impactful use cases for automation and pinpointing obstacles that could slow progress. These steps ensure that companies avoid pursuing projects that do not deliver value.
Phase 1: Use Cases and Discussions with VendorsBefore selecting automation technology, organizations should educate themselves about the capabilities of the automation market. Enter conversations with vendors to gain insight into current offerings that will be most practical for your safety environment. Talking with multiple vendors allows you to build a broad picture of automation capabilities. Frequently, companies fail to educate themselves on this crucial first step. Especially in safety automation, some vendors may lack the experience and ontologies to effectively automate safety surveillance. Therefore, prioritizing vendor conversations is crucial to ensuring you start your investment to deliver its intended value.
Phase 2: Preparing Data and Processing ChangeThe next step in preparing for safety surveillance automation is to ensure data readiness. With your internal data experts and case processing vendors, work to ensure your data is consistent, relevant and within data governance regulations. This includes mapping the path of how data would move through an automated process. Part of this will involve understanding what jobs might be impacted, what tasks may be affected and what metrics will be used to monitor quality and value. Process mapping will allow your safety team to prepare for adjustments and understand the benefits of automation.
As pilot programs are run, continuous monitoring and use of baseline measurements with key performance indicators (KPIs) will be required for tracking reductions and validating change. This process is critical to ensure that the data is truly ready for automation and the vendor’s technology is performing as expected.
Once your organization has established the success of the pilot, ease the technology into your workflow by instituting automation in agreed areas of safety or running it in parallel with the original process for several months. This will provide a benchmark to compare manual versus automated processes and equip your team with enough knowledge and evidence to adapt to the change.
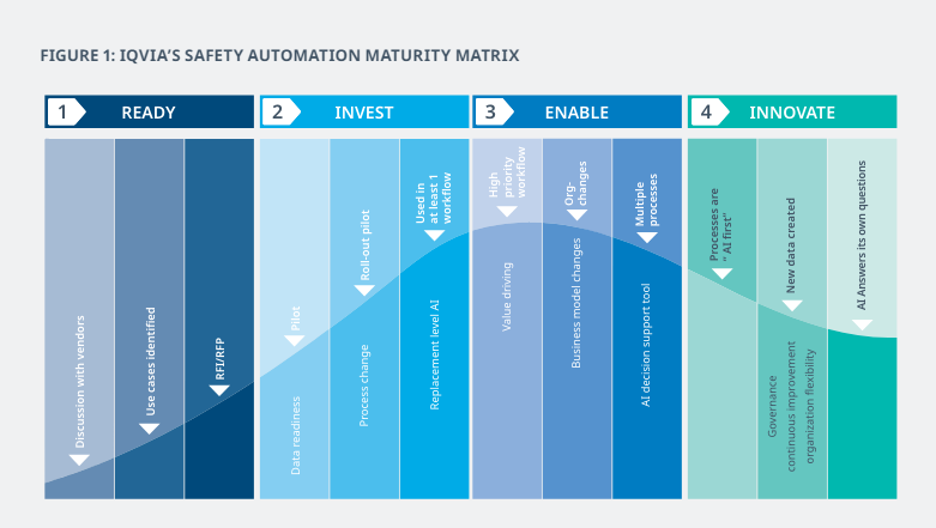 Phase 3: Enable Artificial Intelligence Across the Organization
Phase 3: Enable Artificial Intelligence Across the Organization
Organizations can now focus on high priority workflows in efforts to significantly reduce time and cost while improving quality benefits through automation. At this stage, shifting to consider the entire safety workflow to focus on high value, potentially high-risk projects, will enable organizations to reap the full benefits of automation. This will require building a project framework and governance model for any future artificial intelligence deployment. Monitoring and capturing best practices related to timelines, stakeholder support and vendor management will allow organizations to streamline automation processes, reduce deployment timelines and prevent mistakes from occurring.
Embracing a technology-focused business model enables better identification of automation opportunities. With this technology, organizations can employ fully automated data entry, leverage machine learning algorithms for governance reporting and enable automated case translation and data analysis as critical elements of the safety workflow.
Phase 4: Consider Future Applications of Automation and IntelligenceAs an organization that has implemented automation and intelligence, you can now seek out new ways to actively enhance and accelerate the use of safety data. Organizations should support a constant state of improvement. This can be achieved by dedicating a team to the monitoring of digital innovations and questioning which new technologies carry the potential for added value to the organization. This will encourage vendors to imagine new solutions and advance their own technology roadmaps.
Beginning the process of assessing and implementing automation in your organization’s safety surveillance operations can appear daunting. However, with IQVIA’s Safety Automation Maturity Matrix (SAMM), organizations are provided with a roadmap to better deliver automation through intelligence. Following the outlined phases for implementation will chart a successful course in creating an automated future.
To learn more about IQVIA’s Safety Automation Maturity Matrix, or to learn how IQVIA can help you on this journey, contact Safetypv@iqvia.com or visit iqvia.com.





