





















- Insights
- The IQVIA Institute
- Reports and Publications
- Reports
- Trends in Vaccine Administration in the United States
The COVID-19 pandemic led to an increased role of pharmacies in the overall immunization process as they served as key sites of administration of the COVID-19 vaccines. The Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness (PREP) Act also expanded the role of pharmacists and interns in vaccine administration overall over the course of the pandemic.
This report aims to understand the role of pharmacists in the immunization process by analyzing whether a person received a vaccine at a pharmacy or a medical location for several vaccines between 2018 and 2022 (through the second quarter). The report also analyzes whether there are differences in the site of vaccine administration by gender, income, or race. This analysis provides an understanding of the important role that pharmacies are playing across vaccines and especially for adult vaccines.
Key Findings
Exhibit 1: Number of claims/100,000 eligible persons and % share of adult* vaccines in pharmacy vs. non-pharmacy medical settings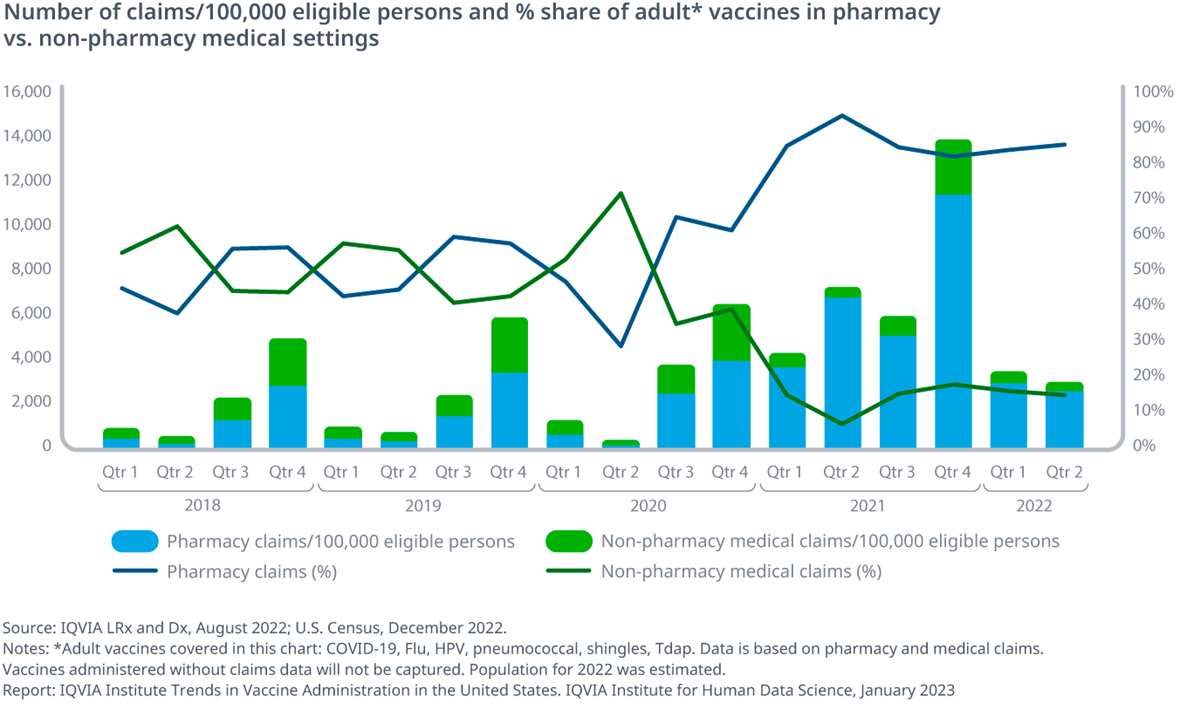
- Overall, across all vaccines for adults in-scope, a large majority of the administration took place at the pharmacy level compared to a non-pharmacy medical setting (Excluding temporary, government public health sites and sites where a claim would not be generated)
- 2020 and 2021 saw a steep increase in vaccine administration at pharmacies due to the COVID-19 vaccine
Exhibit 2: Number of claims/100,000 eligible persons and % share of COVID-19 vaccines for adults in pharmacy vs. non-pharmacy medical settings
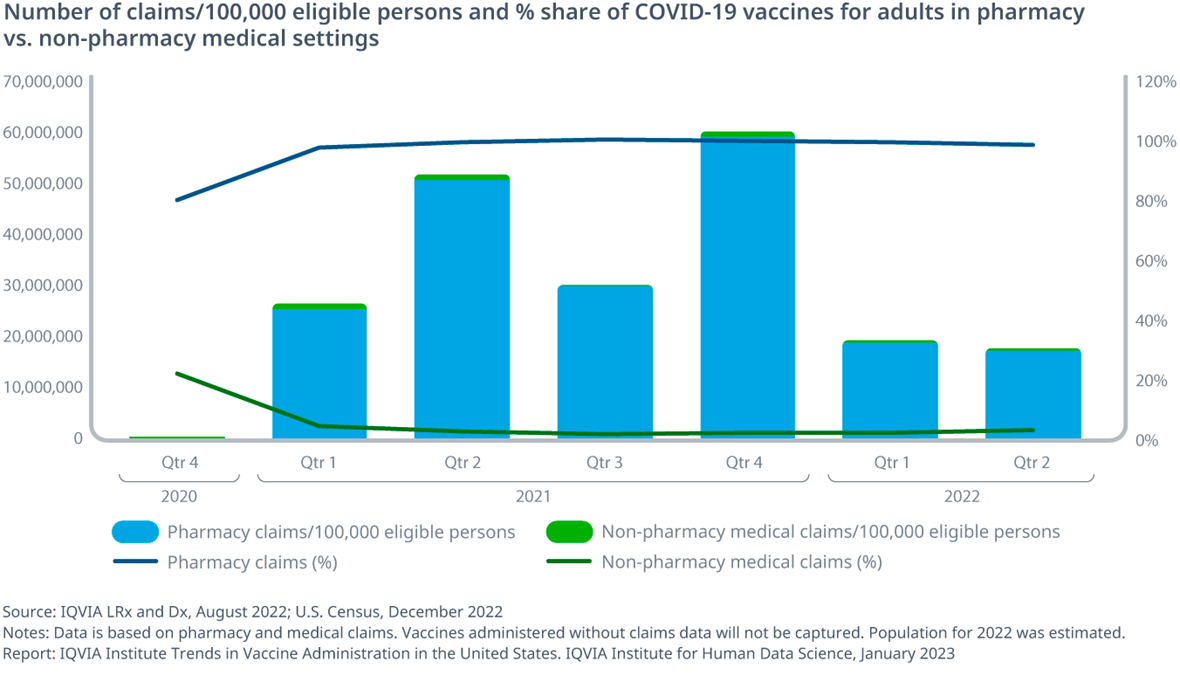
- Many people received COVID-19 vaccines at pharmacies, irrespective of gender, race/ethnicity, or income
- More than 90% of COVID-19 vaccinations provided through either medical centers or pharmacies were delivered at pharmacies (Excluding temporary, government public health sites and sites where a claim would not be generated)
- The Shingles vaccine also saw a similar trend, with a large majority of administration taking place at the pharmacy level across all of the years analyzed
Exhibit 4: Number of claims/100,000 eligible persons and % share of flu vaccines for adults in pharmacy vs. non-pharmacy medical settings
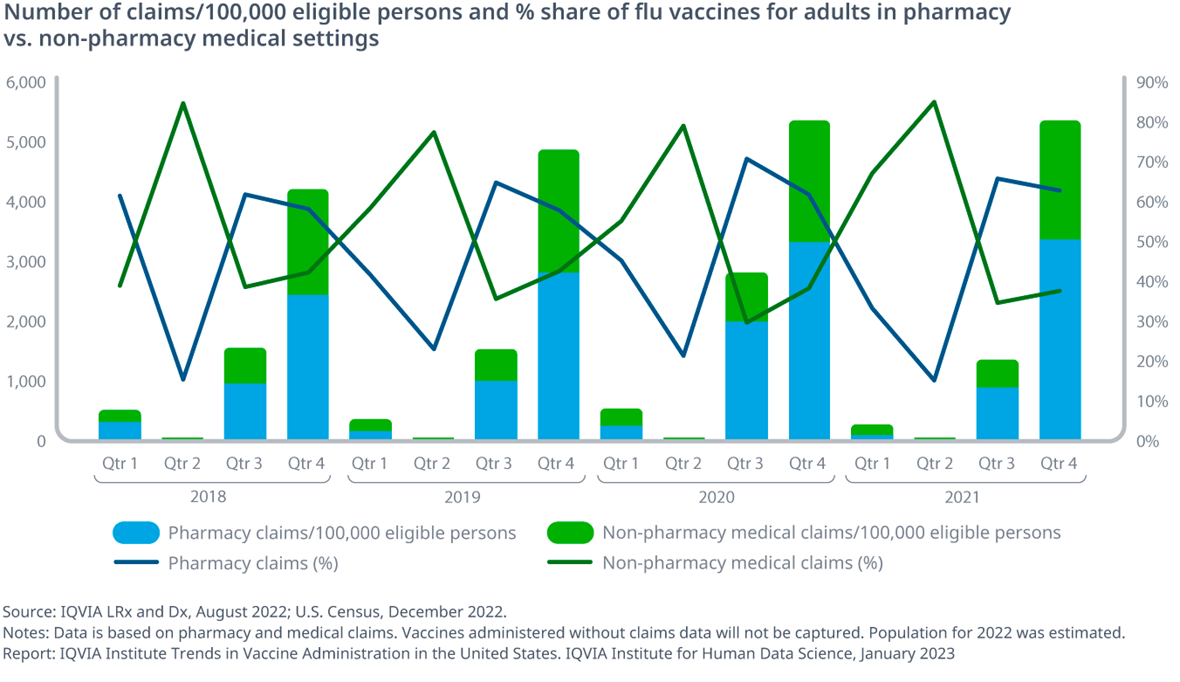
- Pharmacies serve as an important part of the overall flu vaccination process, with 60-70% of vaccinations during flu season (third and fourth quarters) taking place at pharmacies
- The trend in flu vaccine administration at pharmacies also indicates a 30-40% increase in claims for flu vaccines between 2018/19 and 2020
Exhibit 5: Number of claims/100,000 eligible persons and % share of Pneumococcal vaccines for adults in pharmacy vs. non-pharmacy medical settings
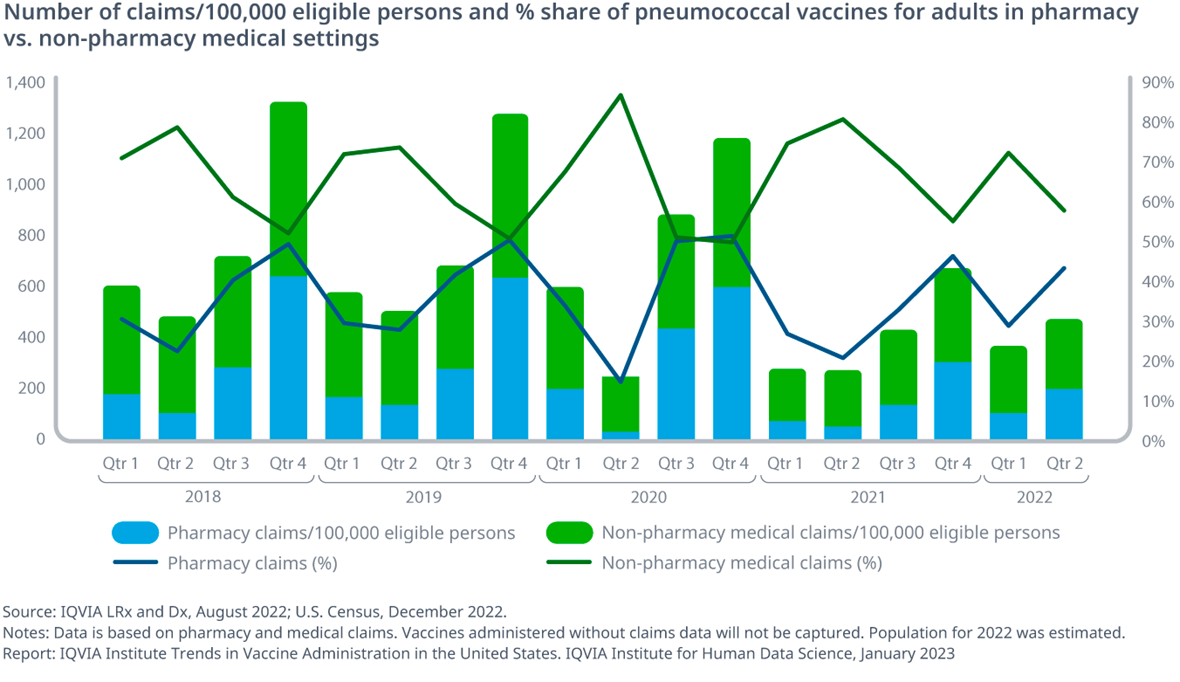
- A large proportion of Pneumococcal vaccine administration also took place at pharmacies. In the third and fourth quarters of any given year, around 40-50% of the administration occurs in a pharmacy setting
- The overall number of claims also consistently increases in these quarters compared to the first and second quarters
- These trends may be associated with the flu season as people may be interacting more with pharmacists for the flu vaccine and may be informed of the Pneumococcal vaccine
- These vaccine administration trends generally hold irrespective of gender, race and income. For some vaccines, Hispanic and Asian American populations see a larger proportion of administration at pharmacies compared to other racial/ethnic categories
Institute Reports
Trends in Global Adult Vaccination
This research brief from the IQVIA Institute – Trends in Global Adult Vaccination: Impact of COVID-19 – aims to provide a baseline of adult vaccination trends and missed vaccination doses during the COVID-19 pandemic while assessing variations by countries and regions.





