





















- Blogs
- Biosimilars to continue rapid growth over the next decade
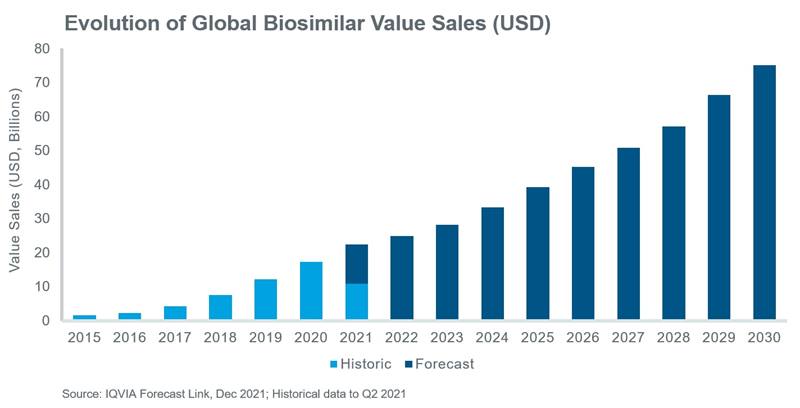
Globally, the uptake of parenteral biosimilars is increasing rapidly and this trend looks set to continue over the next decade. According to IQVIA’s Forecast Link, biosimilar value grew at a CAGR of 78% between 2015 and 2020, reaching approximately $17.9 bn in 2020 and is expected to continue growing at a CAGR of 15% between 2020 and 2030 reaching an estimated $75 bn within the next decade. This article focusses on the recent and anticipated future uptake of biosimilars as well as the diverse rates of uptake that are expected across different geographies and molecules. In addition, the major drivers of this anticipated growth are briefly explored.
Recent biosimilar launches demonstrate a diverse range of uptake depending on the molecule and the geography in which they were launched. Globally, the uptake of biosimilar insulins for diabetes such as insulin glargine and insulin lispro has been slow while the uptake of biosimilars for oncology indications such as bevacizumab, rituximab and trastuzumab has been much more rapid. On average, the uptake of molecules for other indications such as adalimumab, infliximab and teriparatide fall in between these groups.
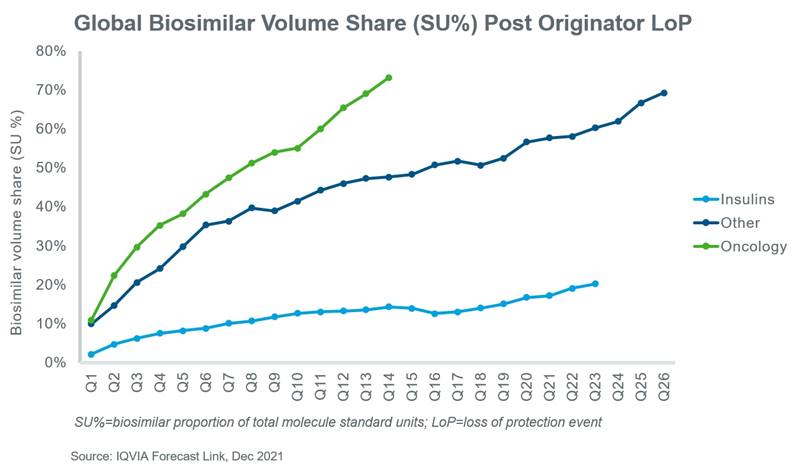
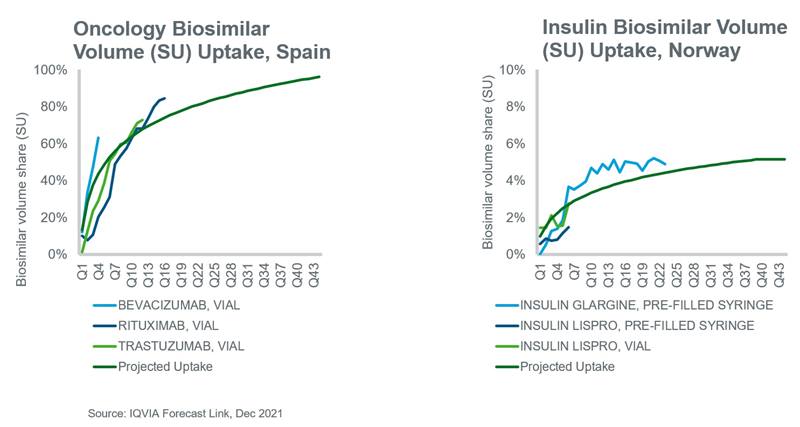
At a country level, there are exceptions to these general observations that can be partially explained by acceptance among prescribers and patients, the strength of policies which encourage their use, price differentials, and whether the country employs a single- or multi-winner tender system. In the case of insulins, there is reluctance among prescribers and patients to use biosimilars due to concerns about safety and disease control1,2 while in Europe for example, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has left decisions about interchangeability and substitution to individual countries.3 Responding to the high cost of biologics for oncology indications, several countries have adopted policies which are increasing the use of biosimilars. For example, in Spain and Poland, biosimilars must be priced at least 25% and 40% below the originator, respectively, and in Norway, oncology biosimilars have secured most hospital contracts thereby driving biosimilar uptake.4
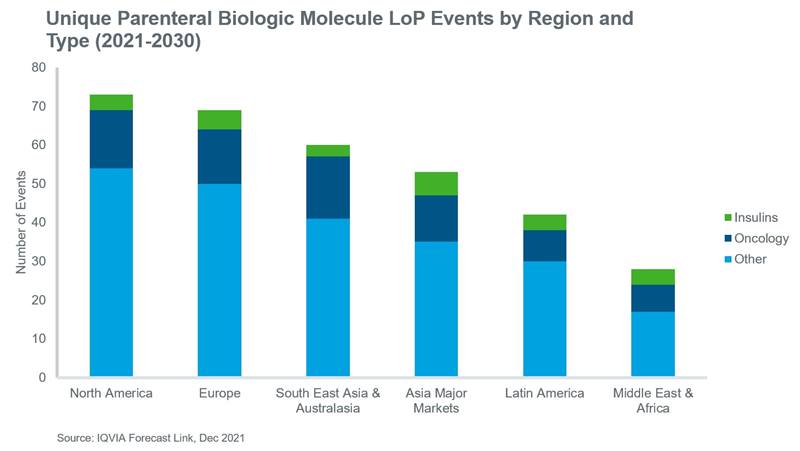
A key driver of biosimilar volume growth over the next decade is the expected number of loss of protection (LoP) events for originator brands. The dates of LoP assumptions in Forecast Link are based not only on key process patent expiries, but also any evidence of biosimilar development in the pipeline. Between 2021 and 2030, these LoP events are likely to impact brands which collectively accounted for global sales of approximately $144 bn in 2020.
IQVIA’s Forecast Link has analyzed the historical uptake of biosimilars at a country level and projected this uptake into the future based on historical trends and the expectations of experts. If appropriate, these assumptions are based on the three groups mentioned above, i.e. oncology, insulin and other molecules. Where historic analogues are not available for a given country, regional averages are employed. These assumptions are then applied to future LoP events where the new biosimilar takes volume share from the originator biologic. Examples of recently adjusted assumptions based on Q2 2021 data are presented in the charts below.
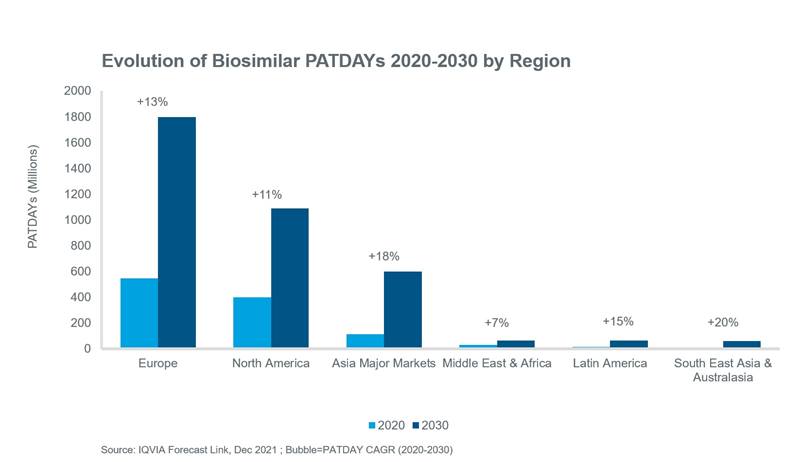
At a regional level, Europe and North America will continue to account for the largest share of global biosimilar volume, although greater rates of volume growth are expected in the major Asian markets, Latin America and South East Asia and Australasia over the next decade.
Although there is much variation in biosimilar uptake based on molecule and geography, there is a high degree of certainty that biosimilar market share will grow significantly over the next decade. A high number of LoP events and more aggressive measures to reduce healthcare expenditure will drive the growth of biosimilars in the foreseeable future.
1 Chaplin, S. Biosimilar Insulins: will switching soon be the norm? Practical Diabetes 2021: 38 (4); 17-20. https://doi.org/10.1002/pdi.2346
2 White J, Wagner A, Patel H. The impact of biosimilar insulins on the diabetes landscape. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Nov 2:1-8. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.21253. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34726499.
3 Why the Reluctance to Use Biosimilar Insulins for Diabetes? https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/906499#vp_1 (accessed Dec 2021)
4 IQVIA Market Prognosis (2021-2025) Country Reports
IQVIA Forecast Link provides regularly updated and fully segmentable sales and volume forecasts across 10,000 products, 600 diseases and 73 countries. Gain insights into current and future market landscapes and power your strategic decision making via this single easy-to-use platform providing unrivalled breadth of coverage. To learn more, please view the Forecast Link Video.





