





















- Blogs
- Global outlook for leading mental health disorders
In 2017, an estimated 792 million people were living with a mental health disorder and this equates to approximately one in ten people globally.1 In terms of prevalence, the top five mental health disorders apart from substance abuse, include anxiety, depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, and collectively these disorders account for 87% of all people living with a mental health condition. The global prevalence of these conditions has remained relatively stable between 1990 and 2017 and therefore the growth in prevalent populations and patient days (PATDAYs) of pharmaceuticals sold are primarily due to growth in populations globally. According to IQVIA’s Forecast Link, these five conditions are also the highest in value sales among mental health disorders in 2020 collectively reaching approximately $38.6bn in sales.
Recently, however, there has been much speculation about the short- and long-term impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic on the prevalence of mental health disorders. For example, at least one study has measured a short-term increase in symptoms of anxiety and depression and the authors assume that the increase in mental health symptoms will continue well beyond the coronavirus outbreak.2 On the other hand, another study concludes that the pandemic has not increased symptom severity compared with pre-pandemic levels.3 Data from IQVIA’s Forecast Link appears to confirm that there has been a noticeable impact from the pandemic as evidenced by increased PATDAY growth in 2020 for all the mentioned conditions except ADHD. Indeed, the impact on anxiety seems to be the most striking and potentially supports one of the previously mentioned findings at least in the short term.
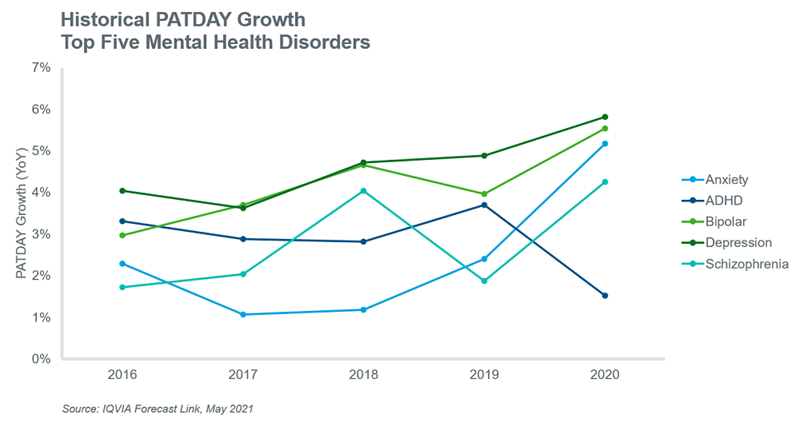
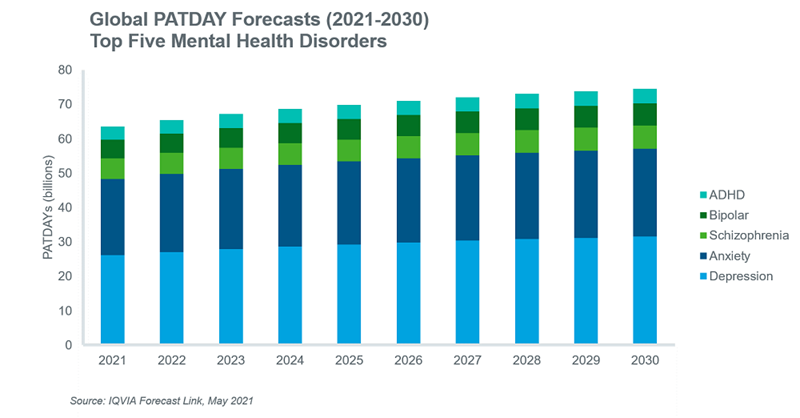
The long-term consequences of the coronavirus pandemic on mental health conditions remains to be seen and a consensus on the likely impact is yet to emerge. However, the short-term impact on PATDAYs is measurable and has been captured in the baseline volume trends for the diseases illustrated below. The most likely scenario, given population growth and the short-term impact of the pandemic, is that historically observed PATDAY growth will continue over the next decade. This will result in increased volume forecasts for the top five mental health disorders.
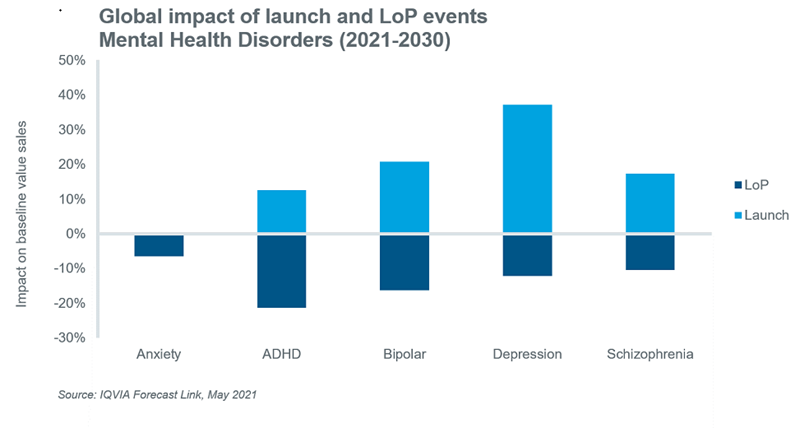
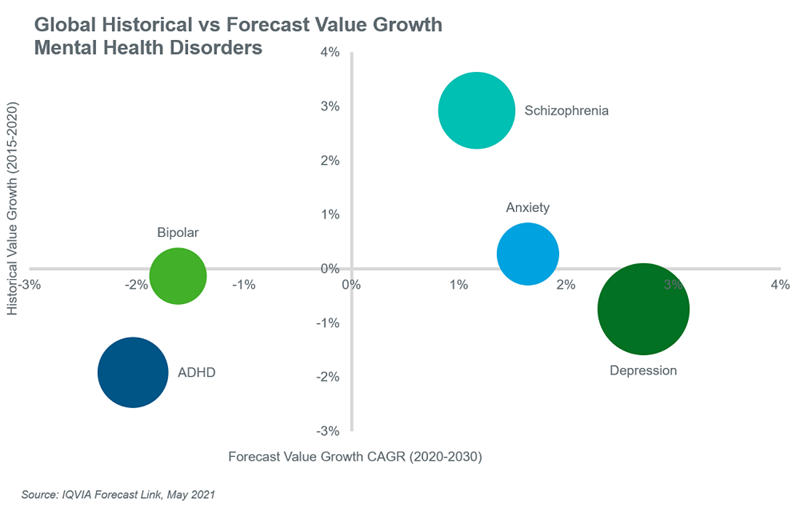
Value sales of pharmaceutical therapies for mental health disorders will be impacted not only by volume forecasts, but new launch and loss of protection (LoP) events, and changes in the implied cost per patient day ($/PATDAY) of existing and new therapies. The net impact of new launch and LoP events on baseline value sales for the top five mental health disorders over the next decade is illustrated below. The net impact of events on value sales is negative for anxiety, ADHD, and bipolar disorder, and positive for depression and schizophrenia. The impact of LoP events will outweigh gains due to new launches particularly in the ADHD and bipolar markets, where a raft of patent expiries is expected in the coming decade. On the other hand, innovative new therapies for depression and schizophrenia will offset value losses due to LoP events resulting in a positive net impact on baseline value sales.
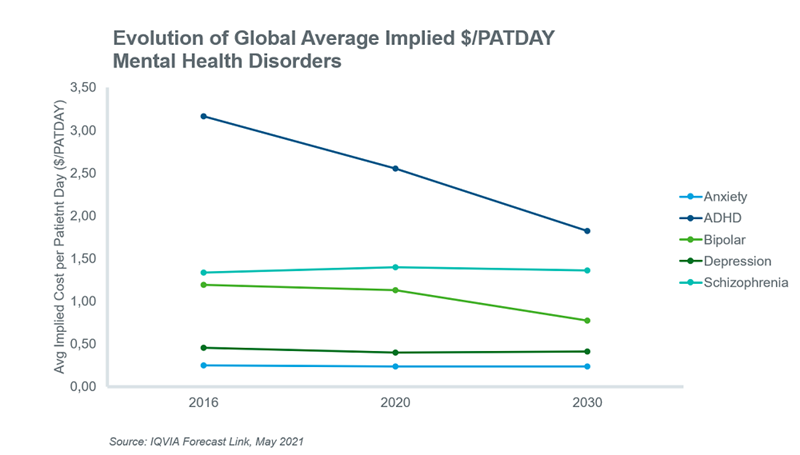
New launches and LoP events will have an important impact on the average implied $/PATDAY of therapies within the top five mental health markets. Generally, LoP events increase competition within the market with the availability of cheaper generic alternatives thereby driving the average implied $/PATDAY down, while newer innovative therapies have the opposite effect because they are usually priced higher than existing therapies. The expected impact of these events and the baseline price forecasts of existing therapies on the average implied $PATDAY over the next decade are shown below. The most dramatic impact on average prices will occur in the ADHD and bipolar markets, where average prices will decrease by 29% and 31%, respectively, over the forecast period.
In conclusion, despite the expected positive PATDAY growth for all the top five mental health disorders, the global outlook for anxiety, depression and schizophrenia is considerably more positive than the outlook for ADHD and bipolar disorders. Although the net impact of events is negative for anxiety, its forecasted PATDAY and price growth are strong enough to offset losses due to LoP events. The depression and schizophrenia markets will experience positive value growth due to new product launches that are expected to be priced higher than existing therapies thereby maintaining or increasing their respective average implied $/PATDAY. While the ADHD and bipolar markets are expected to experience positive PATDAY growth, LoP events and a significantly lower average implied $/PATDAY for both, will result in value contraction in these markets over the next decade.
- Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser (2018) - "Mental Health". Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from: 'https://ourworldindata.org/mental-health' [Online Resource]
- Panchal N, Kamal R, Cox C, Garfield R. The Implications of COVID-19 for Mental Health and Substance Use. Kaiser Family Foundation. Published: February 10, 2021
- Bults M, Beaujean DJ, de Zwart O, et al. Perceived risk, anxiety, and behavioural responses of the general public during the early phase of the Influenza A (H1N1) pandemic in the Netherlands: results of three consecutive online surveys. BMC Public Health. 2011; 11: 2-14





