Bring trials directly to patients to improve access and engagement, increase quality and shorten timelines.






















- Insights
- The IQVIA Institute
- Reports and Publications
- Reports
- Global Trends in R&D 2024: Activity, productivity, and enablers
Biomedical advances are transforming healthcare globally. The multi-stakeholder ecosystem that enables this progress has been buffeted by the global COVID-19 pandemic and is resetting and refocusing on future opportunities to advance the understanding of human biology and disease, discover and develop new therapeutics, and provide evidence of the clinical value of these innovations — for individual patients, populations, and health systems. By all of the traditional metrics, including funding levels, numbers of trial starts, drug launches, R&D success rates, and many others, it is clear that industry and investors continue to see tremendous value in the vast array of ongoing research programs around the world.
This report assesses the trends in new drug launches and the overall number of initiated clinical trials. It also profiles the state of R&D funding and the activity of companies of different types. The results of research are compared to the input effort in a Clinical Development Productivity Index. The notable acceleration and adaptability of the innovation ecosystem is examined in terms of several enablers of R&D productivity, including the relationship between shortening trial durations and the ‘white space’ within clinical development timelines that have been reducing for some diseases and increasing for others.
Key findings:
- Clinical development productivity rose in 2023, primarily due to improvement in the composite success rate which jumped to 10.8%, the highest since 2018.
- Industry and regulatory adoption of innovative and technology-driven enablers, including use of predictive biomarkers, novel trial design, and digital and decentralized trial methodologies contributed to productivity gains.
- A total of 69 novel active substances (NASs) were launched globally in 2023, 6 more than the prior year, and including 24 first-in-class launches in the U.S.
- Clinical development programs among larger biopharma companies are shifting away from areas such as COVID-19 and immuno-oncology to focus on hot spots in oncology and a range of therapies across large population and rare diseases.
- R&D funding levels and deal activity reset in 2023 following a steep decline from peak levels in 2020-21.
Other findings:
M&A activity has rebounded overall with deal value and deal counts rising, while median deal value dipped for the second year
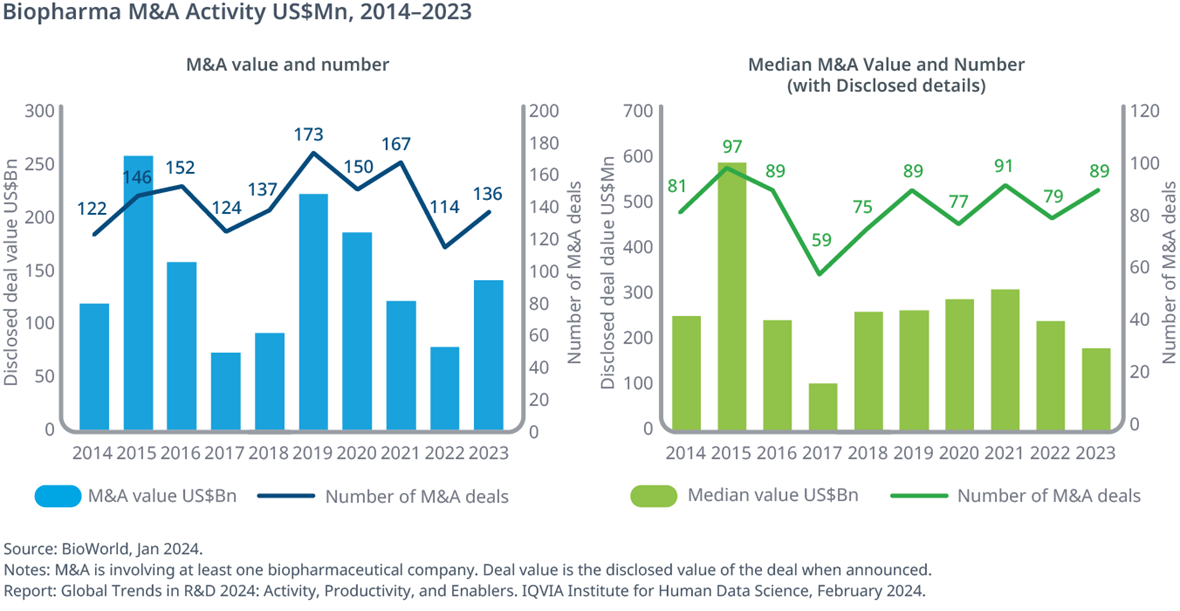
- M&A deal values rebounded to $140Bn in 2023 from a low in 2022 but have not yet reached the levels seen in 2019 and 2020.
- Similarly, the number of M&A deals have slowly decreased since 2019, with an uptick to 136 deals in 2023.
- Although the median disclosed deal value in 2023 of $175Mn was 42% below the $301Mn in 2021, the aggregate deal value increased driven by some very high value deals.
Total clinical trial starts decreased by 15% in 2023, dipping below pre-pandemic level as COVID-19 trial starts slowed
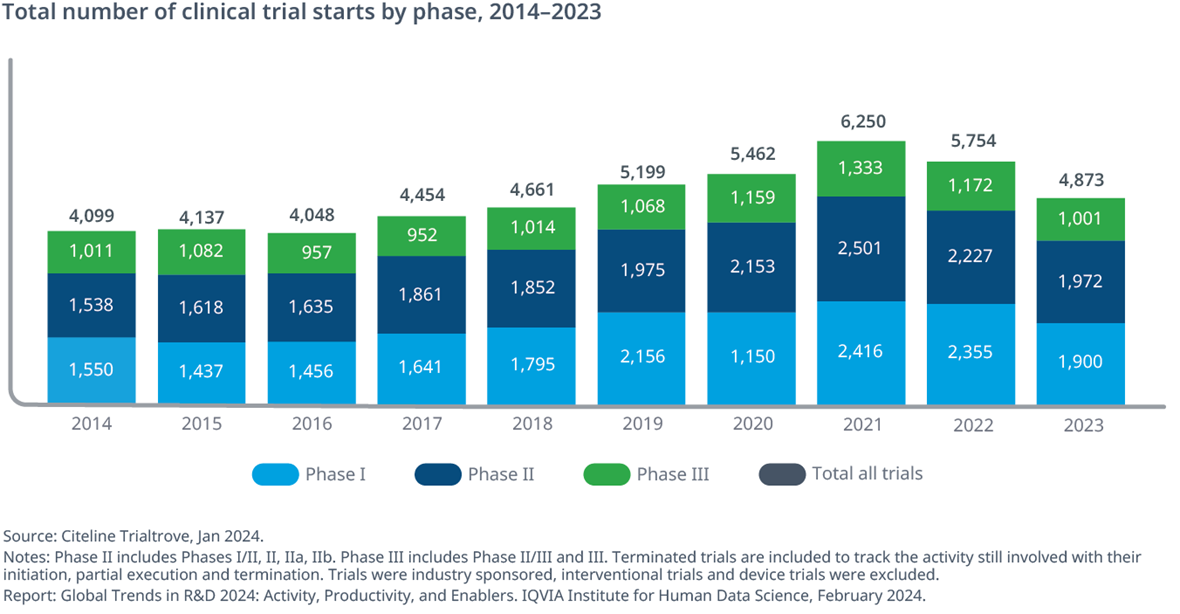
- Clinical trial starts slowed in 2023, with a 15% decline compared to 2022 and down 22% when compared to 2021, with 32% of the decline driven by COVID-19 trials, which have declined 69% compared to 2021 (Exhibit 9).
- Without these COVID-19 trials, trial starts have slowed to below the pre-pandemic level.
- Phase I had the most declines, with 19% fewer than 2022; Phase II activity decreased by 11% and Phase III had a 15% decline in planned or actual trial starts, matching the overall trend.
A total of 69 novel active substances (NASs) were launched globally in 2023
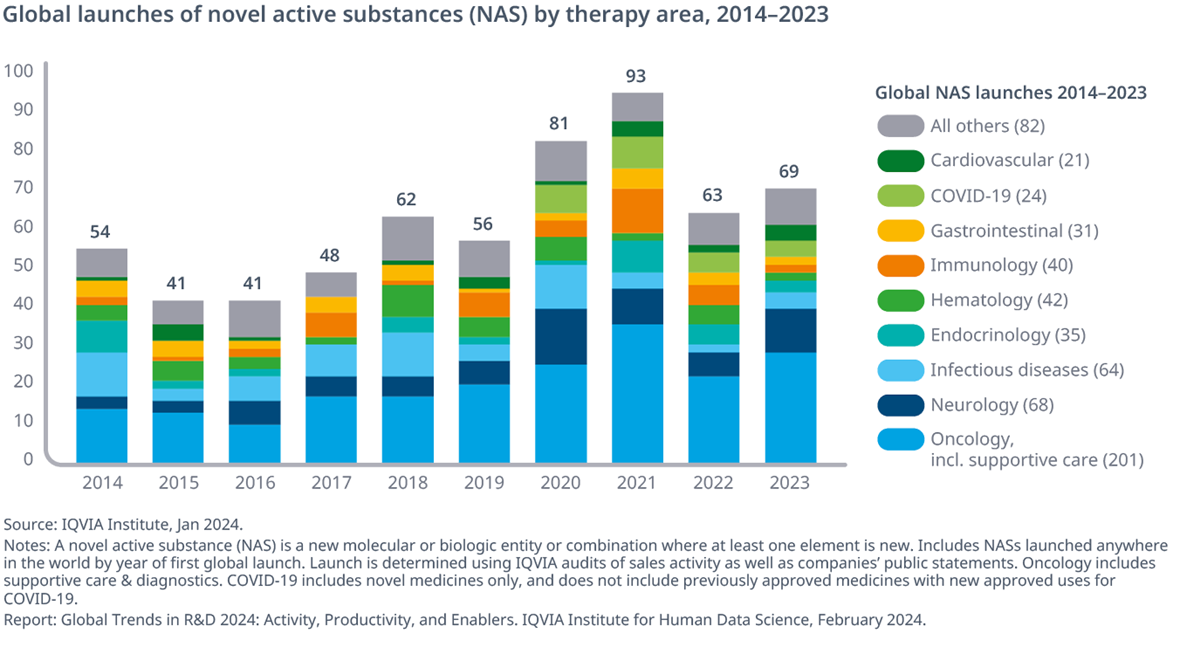
- A total 69 novel active substances (NASs) launched globally in 2023, indicating a rise of 10% from 2022 additionally representing a return to pre-COVID-19 levels.
- Oncology, neurology, and immunology have had rising shares of new launches in the past five years, with 204 of the 362 launches (56%) compared to 105 of 246 (43%) from 2014 to 2018.
- Infectious diseases, including anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-fungal and anti-parasitic treatments, have included novel treatments for HIV, Ebola, and more recently smallpox, and are 11% of NAS launches over the last decade, with some year-to-year variability.
The composite success rate rose to 10.8% in 2023 driven by increases in Phase I, Phase III and regulatory success
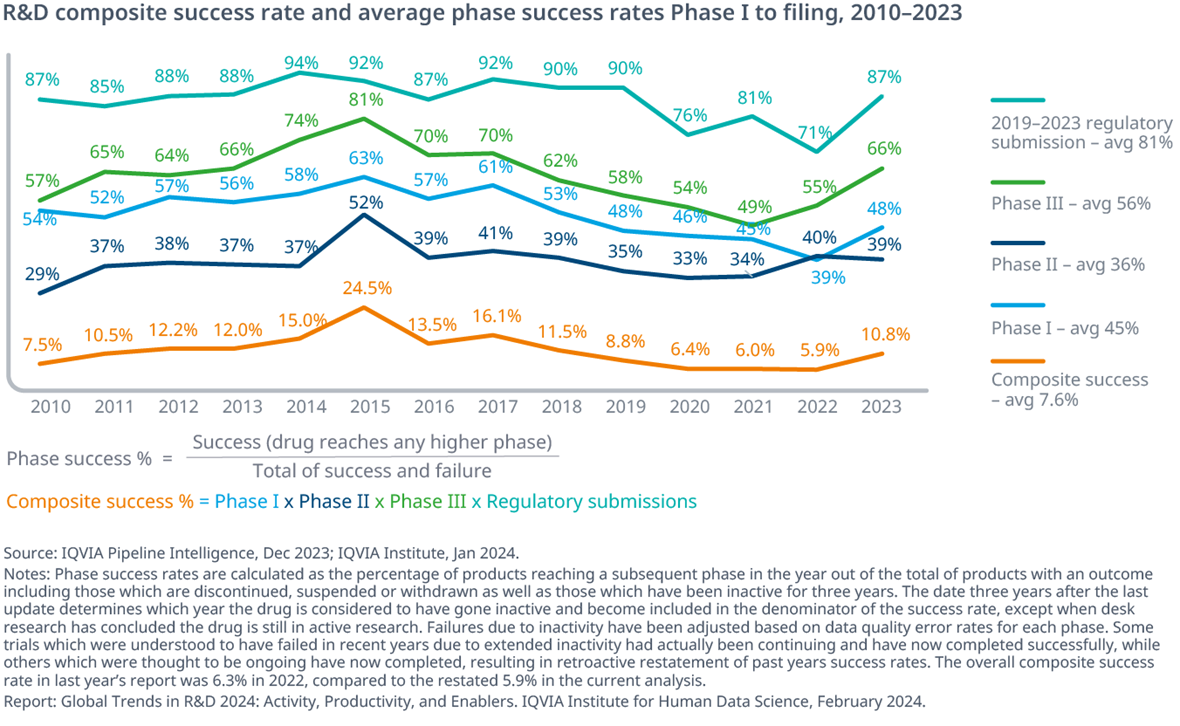
- The composite success rate for the pipeline jumped in 2023 to 10.8% across all therapy areas after falling to a 10-year low in 2022, driven by increases in Phase I, Phase III and regulatory success.
- Phase I success rates rose to 48%, a level last seen in 2019.
- Phase III rates rose to 66%, far above the 56% 10-year pre-pandemic average.
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED IN
Related solutions
Specialized expertise and customized solutions across 14 therapeutic centers of excellence, including oncology, GI/NASH, pediatrics, neurology and rare diseases.





