About the Report
Neuromuscular diseases (NMD) encompass a broad group of disorders that collectively impact an estimated 250,000 patients in United States. Currently, treatment options for these diseases are limited; however, the financial impact is staggering with costs related to neuromuscular disease exceeding $46 billion dollars annually. This new report, funded by the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA), shows that advancements in genetic testing and precision medicine will radically alter the course of neuromuscular disease within the next decade. The report illuminates the role that big data technologies will play in revolutionizing the importance of new-born early genetic screening, intervention and treatment as a pathway to accelerating new therapies. The MDA, with the advent of their comprehensive data hub, MOVR, is driving the advancement of research, new technologies and care strategies to galvanize both the industry and research arenas to pioneer better care and more cures.
Report Summary
Analysis of healthcare charges using IQVIA Real-World Data indicate that total annual charges across all neuromuscular patients exceed $46 billion. Annual medical expenses across NMD groups vary significantly but are upwards of $40,000 annually for the upper quartile in many disease groups. Recent approval of disease-modifying treatments, which can cost upwards of $750,000 per patient per year, are likely to have a significant impact on NMD healthcare spending in the future.
Insights gained from a survey of 90 healthcare professionals focused on the care of patients with NMD – The Neuromuscular Disease Healthcare Provider Survey – sheds light on current care challenges. While improvements in the speed, price and comprehensiveness of available genetic testing is accelerating the process, diagnosis of NMD can often take upwards of a year. Psychological symptoms stand out as an ongoing challenge—affecting 75% of patients and recognized as a high unmet need by 90% of NMD healthcare professionals. Obtaining insurance coverage for new treatments is also a frequent barrier.
This heterogeneity of NMDs combined with the low prevalence of most of the diseases, has made it challenging to determine underlying causes and develop targeted treatments. However, there is now a burgeoning pipeline, with 195 unique molecules currently in development by 165 companies in 20 countries, many of which are ‘Next-Generation’ therapies. As these therapies move through the pipeline, they may face challenges at every level: patient identification and recruitment, selection of appropriate endpoints, integration into the care paradigm and reimbursement from payers. Opportunities that could offset these challenges and promote optimal patient outcomes include widening the use of genetic testing, increasing the use of patient registries, data hubs and other ways to centralize data, and the adoption of technologies for remote appointments and real-time monitoring.
Key Findings
Neuromuscular diseases can manifest in a variety of common symptoms that require specialized care and close management
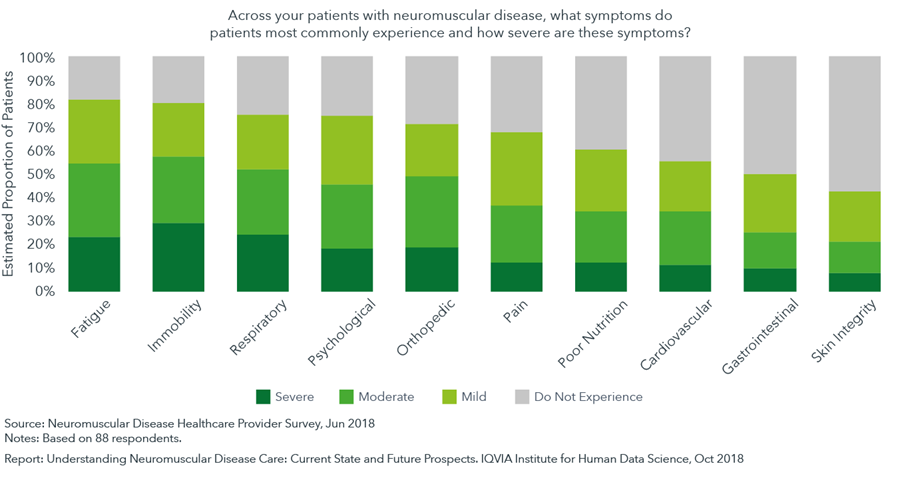
- The signature symptom associated with neuromuscular disease is immobility that compromises dexterity and the ability to walk, caused by progressive worsening of muscle function and weakness.
- According to surveyed healthcare professionals, the most prevalent symptom is fatigue, experienced by 82% of patients, followed by immobility (80% of patients) and respiratory symptoms (75% of patients).
- Psychological symptoms are estimated to affect 75% of patients. As mental health issues comorbid with neuromuscular disease are being increasingly recognized, 60% of respondents rated the unmet need in managing psychological symptoms as high or medium-high.
Analysis of healthcare charges across all neuromuscular diseases indicates annual medical expenditure in the United States in excess of $46 billion
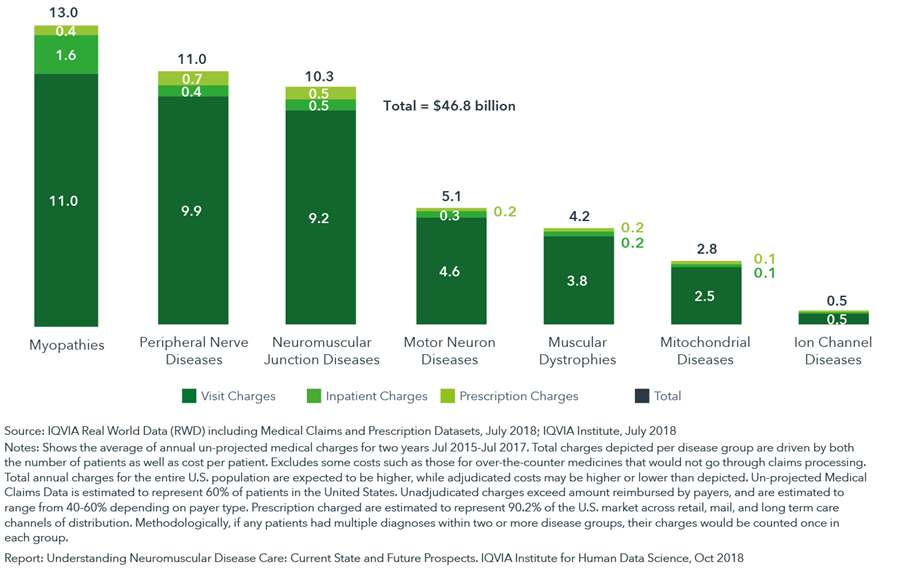
- The associated costs of neuromuscular diseases can be a significant burden to healthcare stakeholders due to the progressive nature of neuromuscular diseases and symptoms that require intensive monitoring and management.
- Annual charges associated with medical care for neuromuscular diseases in the United States greatly exceeded published estimates at more than $46 billion annually, with neuromuscular junction disorders, peripheral nerve diseases and myopathies each accounting for more than $10 billion in charges.
- Previous estimates ranged between $448 million to $1.03 billion per year for individual neuromuscular diseases.
- Annual healthcare charges per patient exceeds $40,000 for the upper quartile of patients, with median estimates between $10,000 and $20,000.
The health journey of a neuromuscular disease patient varies by disease and by individual with many different strategies for diagnosis, care management and treatment
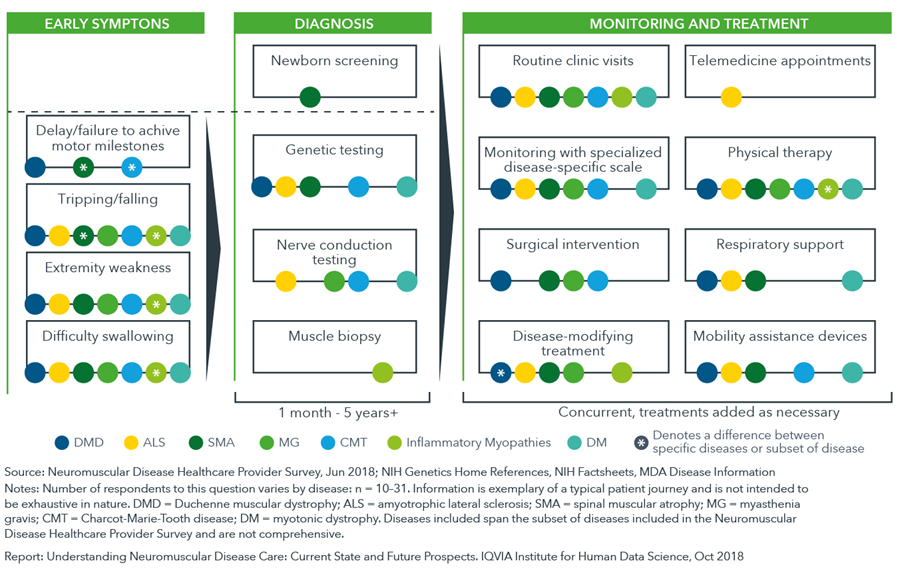
- There is a lag – often more than a year – between a patient’s manifestation of symptoms and their diagnosis with a neuromuscular disease, due to variations in the timing of first symptom appearance, patient genotypes and clinical manifestations.
- Genetic testing and newborn screening is an option for many neuromuscular diseases with Pompe disease, spinal muscular atrophy, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency all included on a core screening panel of diseases recommended for newborns in the United States (Recommended Uniform Screening Panel, RUSP).
- Diversity in treatment and monitoring approaches is caused by many factors including disease subtype, inter-individual variability in symptom or disease progression, ambiguity in treatment guidelines and differences in patient access to care.
Globally, over 190 unique candidates are being evaluated for neuromuscular diseases, with R&D activity heavily concentrated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy
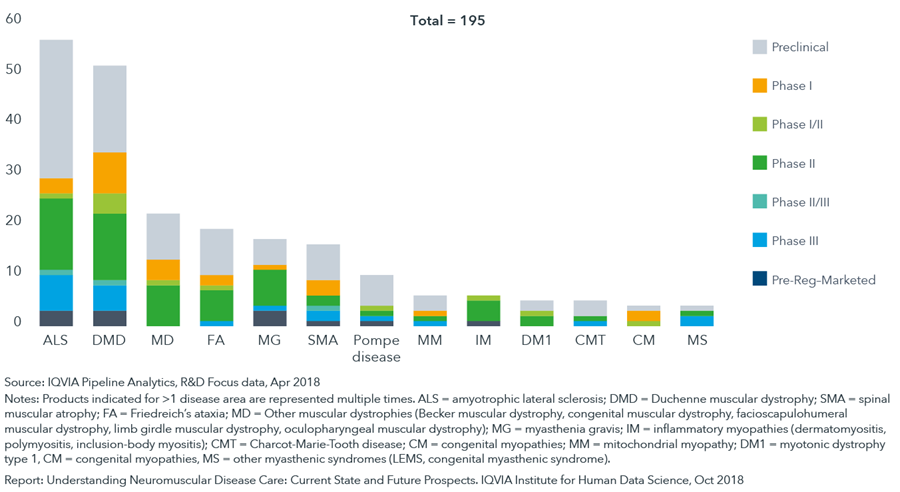
- A broad drug-development pipeline is emerging across neuromuscular diseases in part due to improvements in the genetic understanding of neuromuscular diseases and technological advances.
- The number of molecules in clinical development increased five-fold from approximately 20 in 2013 to the approximately 100 seen in this analysis in 2018.
- While the bulk of the pipeline is centered on small molecules (43%), gene therapies and antisense oligonucleotides make up 23%.
Respondents to the Neuromuscular Disease Healthcare Provider Survey recognized the potential for improvements in both diagnosis and care management, particularly around genetic screening and improvements in insurance coverage.
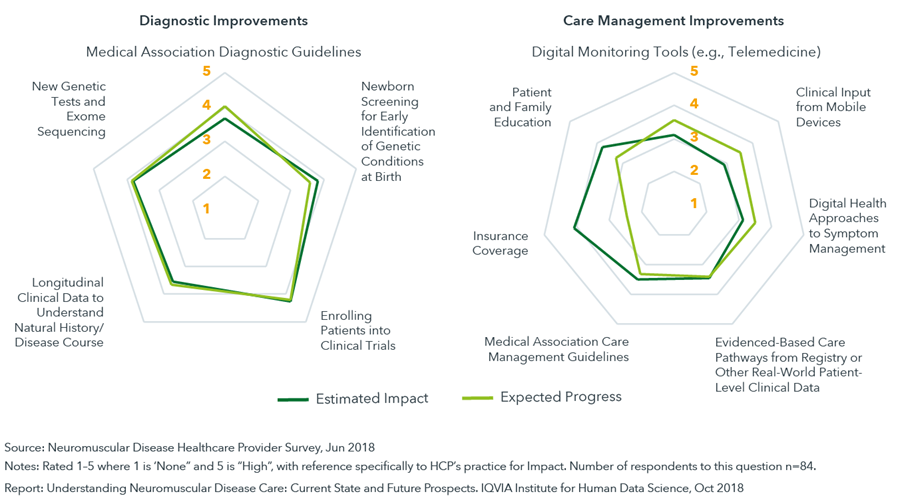
- An improved understanding of disease and advances in technology have invigorated the drug development pipeline for neuromuscular disease, offering the potential to transform care within the next decade.
- Employing effective newborn screening programs will enable patients to be diagnosed sooner and lead to a broader understanding of disease characteristics within the general population.
- Digital health solutions including telemedicine offer innovative approaches for monitoring, measuring and patient support have the potential to offer significant advances in care management.
- Increasing the use of patient registries/data hubs and improving longitudinal patient data will help in the understanding of the natural history of these diseases.